
By depreciating these assets, businesses can accurately reflect their decreasing value on their financial statements and ensure a realistic representation of their net worth. The hottest retail item of today can be relegated to nostalgia channels on YouTube tomorrow. And when your business still has some of these outdated, unwanted, or unusable items in your inventory, you’ll want to offset the lost value of these assets in your general ledger and balance sheet. So rather than adjusting your Inventory account, you would update its contra account — Obsolete Inventory. By considering these contra accounts, a business can maintain accurate and reliable financial statements, which is crucial for making informed decisions such as budgeting, forecasting, and resource allocation.
Depreciation and Accumulated Depreciation Example
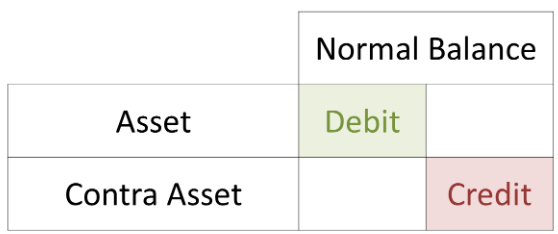
Contra asset accounts include allowance for doubtful accounts and accumulated depreciation. Contra asset accounts are recorded with a credit balance that decreases the balance of an asset. A key example of contra liabilities includes discounts on notes or bonds payable. There are four key types of contra accounts—contra asset, contra liability, contra equity, and contra revenue. Contra assets decrease the balance of a fixed or capital asset, carrying a credit balance. Contra asset accounts include allowance for doubtful accounts and the accumulated depreciation.
What is contra accounts receivable
You currently use the income statement method toestimate bad debt at 4.5% of credit sales. You are consideringswitching to the balance sheet aging of receivables method. Thiswould split accounts receivable into three past- due categories andassign a percentage to each group.
Accounting Entries for Contra Assets
The purpose of a contra asset account is to store a reserve that reduces the balance in the paired account. By stating this information separately in a contra asset account, a user of financial information can see the extent to which a paired asset should be reduced. Contra equity is a general ledger account with a debit balance that reduces the normal credit balance of a standard equity account to present the net value of equity in a company’s financial statements. Examples of equity contra accounts are Owner Draws and Repurchased Treasury Stock Shares. A liability that is recorded as a debit balance is used to decrease the balance of a liability. It is not classified as a liability since it does not represent a future obligation.
Risk Classification Method
Whenever an organization buys an asset and depreciates it over the asset’s useful economic life, the reduction in value accumulates over the year, which is called accumulated depreciation. The accumulated depreciation balance cannot exceed the book value of the asset. We get the remaining value of assets by deducting the accumulated depreciation balances from the book value of the asset.
They are also the result of globally accepted accounting principles for accurately reporting financial numbers. As we have seen in the above discussion, how reporting contra assets accounts helps in a better understanding of the financial statements of any organization. So, an organization looking where do contra assets go on a balance sheet for a robust accounting process must move to this reporting for better understanding. In business bookkeeping, contra asset accounts play a crucial role in managing financial data and guiding strategic decisions by providing a clear picture of the true value of assets and net revenue.
- In accordance with the matching principle of accounting, this ensures that expenses related to the sale are recorded in the same accounting period as the revenue is earned.
- Contra liabilities are common in companies that sell bonds to raise capital.
- By keeping the original dollar amount intact in the original account and reducing the figure in a separate account, the financial information is more transparent for financial reporting purposes.
- The first step in accounting for the allowance for doubtful accounts is to establish the allowance.
- As assets like machinery, equipment, or buildings wear out or become obsolete, their value decreases.
- This make sense because Home Depot wouldn’t be carrying accounts receivable with long payment terms.
When a bond is issued at less than its face value, the amount of the discount is recorded as a contra liability. This reduces the overall liability on the balance sheet and represents the reduced amount that will eventually need to be repaid. The list of asset accounts on your general ledger and balance sheet conveys the combined, potential value of all of the tangible and intangible items that your organization possesses. But in the real world, converting all of that potential into hard cash is highly unlikely, if not impossible.
Rent is typically recorded as an expense on the income statement and reduces the net income of a company. It is commonly used to offset the value of a long-term asset, reducing its carrying value. This contra account allows for a more accurate representation of the asset’s value as it accounts for its wear and tear or obsolescence. To fully comprehend the enigma that is a contra asset, let’s start from the beginning.
When the estimation isrecorded at the end of a period, the following entry occurs. For example, a customer takes out a $15,000 car loan on August1, 2018 and is expected to pay the amount in full before December1, 2018. For the sake of this example, assume that there was nointerest charged to the buyer because of the short-term nature orlife of the loan. When the account defaults for nonpayment onDecember 1, the company would record the following journal entry torecognize bad debt.



